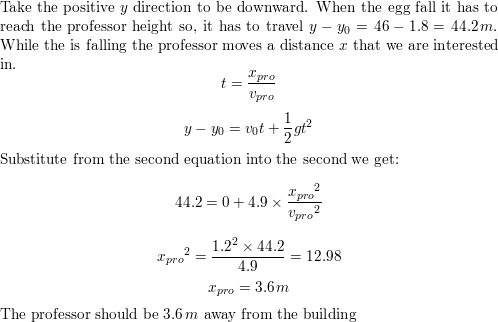Physics Equation For Falling Off A Roof

Calculating time taken to fall distance h.
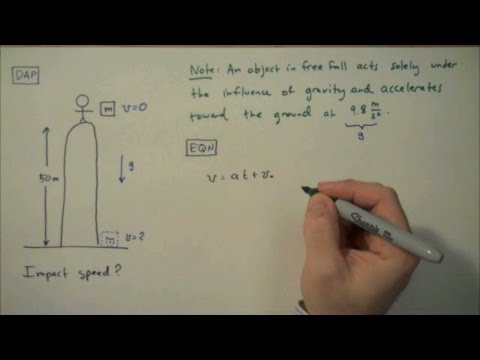
Physics equation for falling off a roof. The variables include acceleration a time t displacement d final velocity vf and initial velocity vi. By applying the kinematics developed so far to falling objects we can examine some interesting situations and learn much about gravity in the process. A set of equations describe the resultant trajectories when objects move owing to a constant gravitational force under normal earth bound conditions for example newton s law of universal gravitation simplifies to f mg where m is the mass of the body this assumption is reasonable for objects falling to earth over the relatively short vertical distances of our everyday experience but is. T v v i g see derivation of velocity time gravity equations for details of the derivation since the initial velocity v i 0 for an object that is simply falling the equation reduces to.
Each equation contains four variables. S h. If values of three variables are known then the others can be calculated using the equations. The equation v u at can t be used because t is unknown so use the equation v2 u2 2as.
Calculating instantaneous distance fallen. But using this equation i can put in my values for the starting and ending y position as well as the initial y velocity and solve. Taking the square root of both sides. So s gt2.
Free falling objects physics lesson 5. T stands for the fall time measured in seconds. From the definition of velocity we can find the velocity of a falling object is. V is the initial velocity measured in m s or ft s.
The car drives straight off the edge of a cliff that is 57 m high. V 2gh this is the final velocity. Paul bogdan 4 479 views. Falling objects form an interesting class of motion problems.
For example we can estimate the depth of a vertical mine shaft by dropping a rock into it and listening for the rock to hit the bottom. Kinematic equations relate the variables of motion to one another. How fast was the car traveling when it went over the cliff. Equation story problem 9 falling object.
Time with respect to velocity. The general gravity equation for elapsed time with respect to velocity is. S ut at2 0t gt2. The investigator at the scene of the accident notes that the point of impact is 130 m from the base of the cliff.
Without the effect of air resistance each object in free fall would keep accelerating by 9 80665. The physics of jumping off an 8 story building and not dying. G is the free fall acceleration expressed in m s or ft s.